Managing Rosacea in Seniors: Prevention Tips and Effective Treatments
According to Wiley, the prevalence of rosacea rises dramatically with age, from 0.3% in 16–29 years old to 5.7% in 60–70 years old. Seniors with rosacea may experience significant symptoms, including redness and visible blood vessels. This blog will help seniors manage their rosacea effectively by providing advice on avoiding flare-ups and efficient treatments. We'll delve into triggers, skincare practices, treatment alternatives, and lifestyle modifications crucial in promoting transparent, healthy skin.
Understanding Rosacea
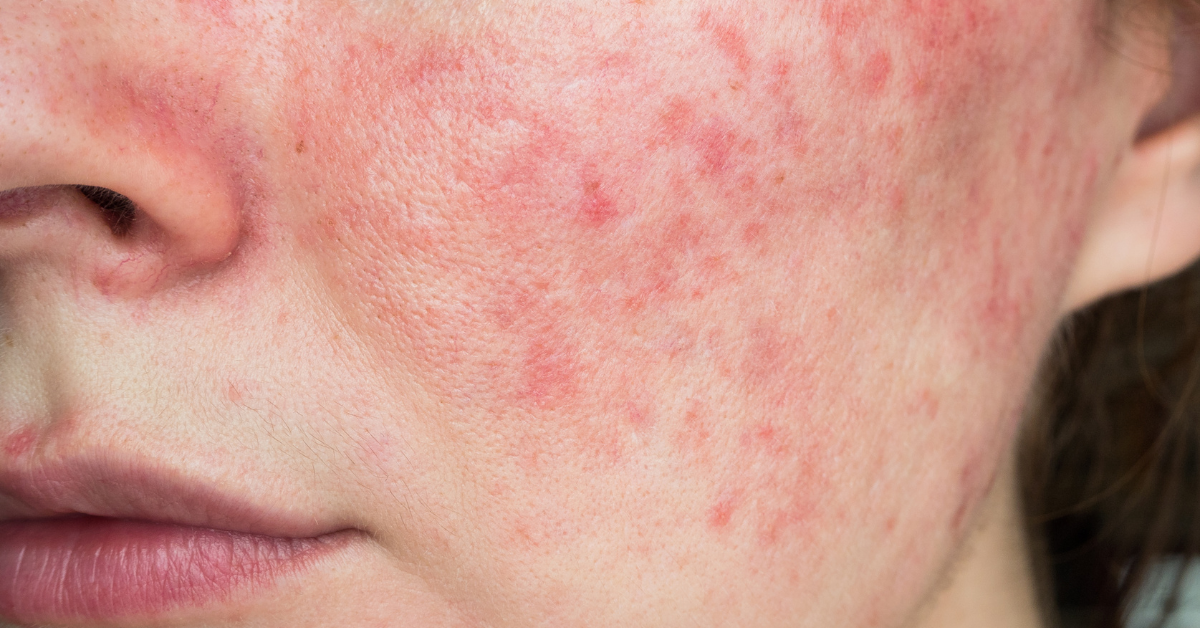
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face and is characterized by redness, visible blood vessels, and occasionally pimples or lumps. Older adults may experience milder symptoms or confuse it with other skin conditions. To effectively manage their rosacea, seniors must understand and manage their triggers, such as alcohol, spicy foods, and sun exposure.
Prevention Tips for Rosacea
Effective rosacea management frequently starts with prevention. Seniors can reduce flare-ups and preserve good skin by implementing the following essential strategies:
Sun Protection: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30+ every day. Choose sunscreens with mineral bases; these are better for delicate skin.
Avoiding Triggers: Recognize and stay away from typical triggers, such as hot or cold foods, alcohol, and trigger situations. Maintain a journal to monitor and control your triggers.
Skincare Routine: Use moisturizers without scent and gentle, non-abrasive cleansers. Select items marked "sensitive skin."
Dietary Considerations: Consume foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, and vegetables, as these reduce inflammation. Avoid hot beverages and spicy foods, as they may cause flare-ups.
Effective Treatments for Rosacea
Effective rosacea management entails a mix of topical remedies, oral drugs, and occasionally sophisticated therapies. Here is a thorough examination of each available treatment:
Topical Medications:
Metronidazole: an antibiotic applied that lessens redness and irritation.
Azelaic Acid: aids in treating acne-like symptoms and reducing inflammation.
Oral Medications:
Antibiotics: Oral antibiotics such as minocycline or doxycycline can manage more severe cases of rosacea and control inflammation. They are usually only recommended temporarily.
Isotretinoin: Strong retinoid isotretinoin may be used in extreme situations, particularly when other therapies fail to control inflammation and redness.
Laser and Light Therapy:
Pulsed Dye Laser: reduces skin redness and the appearance of blood vessels by focusing on blood vessels.
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): targets pigment and blood vessels to help enhance skin texture and lessen redness.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Stress Management: Use stress-reduction strategies such as frequent exercise, deep breathing, and meditation. Engaging in exciting hobbies and activities can also help.
Regular Check-Ups: Make routine dermatologist appointments to monitor symptoms and modify your care as necessary. Record flare-ups and possible triggers so you can talk to your doctor about them.
Gentle Skin Care: Use calming, non-irritating skincare products, avoiding those containing alcohol or robust scents. Regular moisturizing also helps preserve the skin barrier.
Diet and Nutrition: Consume a well-balanced diet high in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids. Keep a diet journal to identify problem foods and avoid well-known triggers like alcohol and spicy foods.
When to Seek Professional Help
While lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications can help manage rosacea, there are some circumstances in which speaking with a healthcare provider is essential. Seniors have to get expert assistance if
Persistent Symptoms: A dermatologist can offer more sophisticated treatment choices and modifications to the current regimen if the condition worsens or if rosacea symptoms continue after adhering to a thorough treatment plan.
Severe Symptoms: A medical professional must evaluate intense redness, swelling, or lumps related to severe flare-ups. More potent drugs or specialized treatment may be necessary to eliminate these symptoms.
Eye Involvement: Ocular rosacea is one of the conditions that can result from rosacea. If you experience discomfort, dryness, or redness in the eyes, consult a healthcare professional to manage the condition appropriately.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Preventive interventions, appropriate medications, and lifestyle adjustments are necessary for managing rosacea in older adults. By protecting their skin from triggers, using the right skincare products, and considering medical and professional therapy, seniors can effectively control their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Routine medical check-ups further support healthy skin maintenance.
Share this blog with your family and friends so they can learn the preventive tips and effective treatments for managing rosacea in seniors.
If you want to read more helpful blogs like this, check out our News and Resources section and become a better and brighter person.